网站首页 文章专栏 学习理解 Spring ApplicationListener,以及 ApplicationListener在soul网关的应用
一. ApplicationContext是什么
ApplicationContext事件机制是观察者设计模式的实现,通过ApplicationEvent类和ApplicationListener接口,可以实现ApplicationContext事件处理。
如果容器中有一个ApplicationListener Bean,每当ApplicationContext发布ApplicationEvent时,ApplicationListener Bean将自动被触发。这种事件机制都必须需要程序显示的触发。
其中spring有一些内置的事件,当完成某种操作时会发出某些事件动作。比如监听ContextRefreshedEvent事件,当所有的bean都初始化完成并被成功装载后会触发该事件,实现ApplicationListener
同样事件可以自定义、监听也可以自定义,完全根据自己的业务逻辑来处理。
| Spring 内置事件 | 描述 |
| ContextRefreshedEvent | ApplicationContext 被初始化或刷新时,该事件被发布。这也可以在 ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中使用 refresh() 方法来发生。此处的初始化是指:所有的Bean被成功装载,后处理Bean被检测并激活,所有Singleton Bean 被预实例化,ApplicationContext容器已就绪可用 |
| ContextStartedEvent | 当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext (ApplicationContext子接口)接口中的 start() 方法启动 ApplicationContext 时,该事件被发布。你可以调查你的数据库,或者你可以在接受到这个事件后重启任何停止的应用程序。 |
| ContextStoppedEvent | 当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口中的 stop() 停止 ApplicationContext 时,发布这个事件。你可以在接受到这个事件后做必要的清理的工作。 |
| ContextClosedEvent | 当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext 接口中的 close() 方法关闭 ApplicationContext 时,该事件被发布。一个已关闭的上下文到达生命周期末端;它不能被刷新或重启。 |
| RequestHandledEvent | 这是一个 web-specific 事件,告诉所有 bean HTTP 请求已经被服务。只能应用于使用DispatcherServlet的Web应用。在使用Spring作为前端的MVC控制器时,当Spring处理用户请求结束后,系统会自动触发该事件。 |
| ApplicationStartedEvent | spring boot启动开始时执行的事件 |
ApplicationListener是一个接口,里面只有一个onApplicationEvent方法。如果在上下文中部署一个实现了ApplicationListener接口的bean,那么每当在一个ApplicationEvent发布到 ApplicationContext时,调用ApplicationContext.publishEvent()方法,这个bean得到通知。类似于Oberver设计模式。其接口定义如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener extends EventListener {
void onApplicationEvent(E var1);
}二. ApplicationContext能做什么
1). 可以根据内置的事件类型,在ApplicationContext bean被初始化的时候做某些操作,发送消息,初始化bean等等
2). 可以在springboot初始化加载完成后,进行某些操作
3). 可以在web服务请求被响应后,做某些事件
4). 可以根据自定义事件类型,发布事件,监听到事件后触发某些操作等等,这也是最常见的使用
三. ApplicationContext的demo
1). 体验spring 内置事件
定义ApplicationStartedEventListener监听器,实现ApplicationListener接口,且在接口泛型定义ApplicationStartedEvent,就是内置的事件。注意要使用 @Component将listener被springboot感知注入
@Component
public class ApplicationStartedEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent event) {
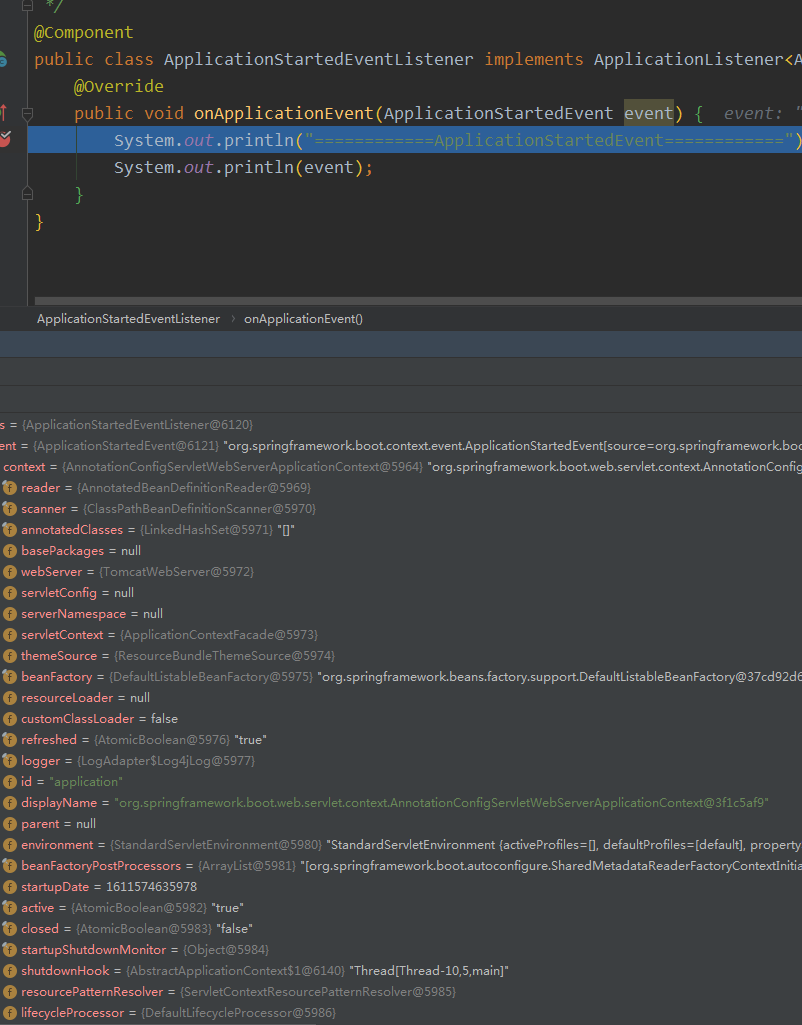
System.out.println("============ApplicationStartedEvent============");
System.out.println(event);
}
}2). 同样的代码我们多搞几份,更改监听的事件类型
@Component
public class ContextClosedEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextClosedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextClosedEvent contextClosedEvent) {
System.out.println(contextClosedEvent);
System.out.println("=============contextClosedEvent............................");
}
}
@Component
public class ContextRefreshedEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
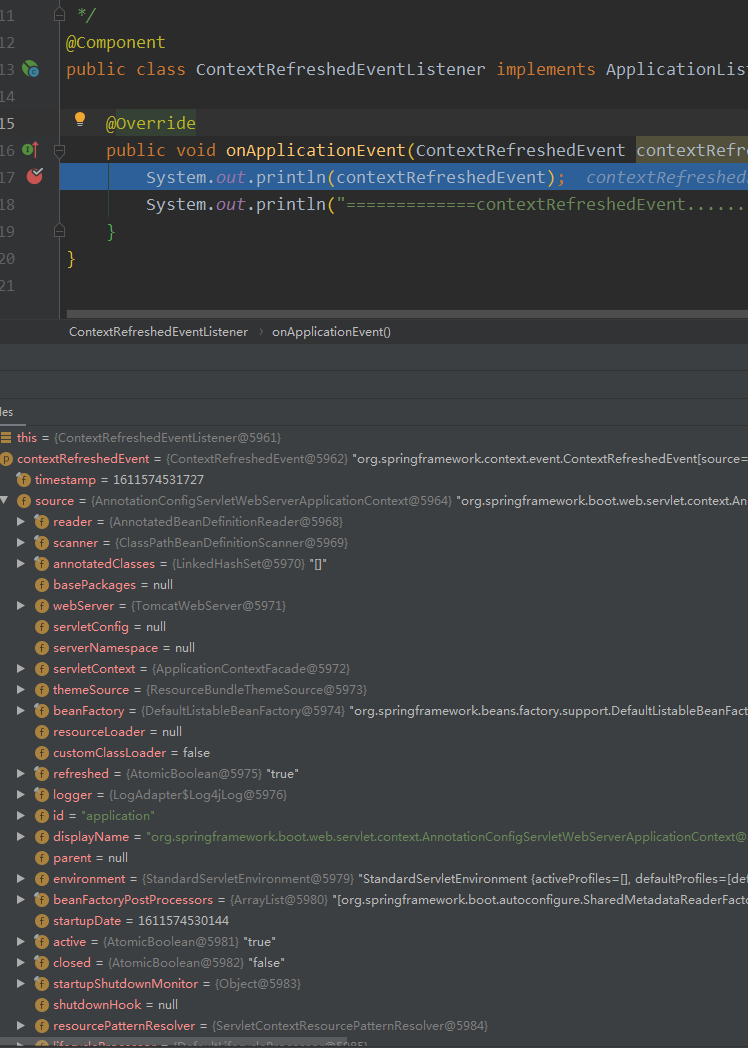
System.out.println(contextRefreshedEvent);
System.out.println("=============contextRefreshedEvent............................");
}
}
@Component
public class RequestHandledEventListener implements ApplicationListener<RequestHandledEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(RequestHandledEvent requestHandledEvent) {
System.out.println(requestHandledEvent);
System.out.println("=============requestHandledEvent............................");
}
}以上的事件分别为:
1>. ApplicationStartedEvent:spring boot启动开始时执行的事件
2>. ContextClosedEvent: 一个已关闭的上下文到达生命周期末端
3>. ContextRefreshedEvent: ApplicationContext 被初始化或刷新时
4>. RequestHandledEvent: 在使用Spring作为前端的MVC控制器时,当Spring处理用户请求结束后,系统会自动触发该事件
然后启动项目
发现先走到了 ContextRefreshedEvent
然后走到 ApplicationStartedEvent
日志打印:
2021-01-25 19:37:17.598 INFO 10532 --- [ main] o.s.s.c.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor : Initializing ExecutorService 'applicationTaskExecutor' 2021-01-25 19:37:17.716 DEBUG 10532 --- [ main] inMXBeanRegistrar$SpringApplicationAdmin : Application Admin MBean registered with name 'org.springframework.boot:type=Admin,name=SpringApplication' org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext@3f1c5af9, started on Mon Jan 25 19:37:15 CST 2021] =============contextRefreshedEvent............................ 2021-01-25 19:38:01.149 INFO 10532 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.e.t.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8888 (http) with context path '' 2021-01-25 19:38:01.152 INFO 10532 --- [ main] y.TestserviceApplication : Started TestserviceApplication in 46.326 seconds (JVM running for 47.793) ============ApplicationStartedEvent============ org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartedEvent[source=org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication@54089484]
然后请求一个web接口:
http://127.0.0.1:8888/test/get
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@PostMapping("/get")
public BaseResponse get(){
Map res = new HashMap<>();
res.put("name","yx");
return BaseResponse.success(res);
}
}发现,先走到
res.put("name","yx");在返回response之前,进入事件监听
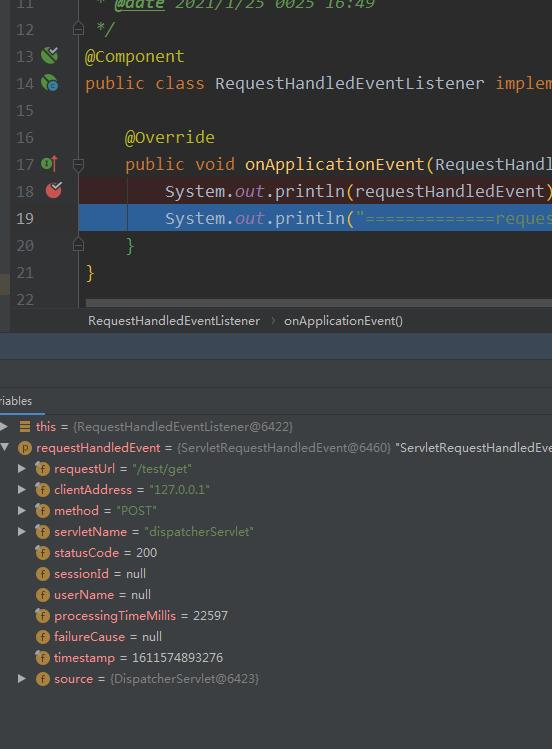
日志打印:
ServletRequestHandledEvent: url=[/test/get]; client=[127.0.0.1]; method=[POST]; servlet=[dispatcherServlet]; session=[null]; user=[null]; time=[22597ms]; status=[OK] =============requestHandledEvent............................
从上面的demo可以看出,几个事件都按照说明实际执行了。我们再来体验下自定义事件。
2). 自定义事件监听
1>. 定义事件类型
public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String name;
public MyEvent(Object source, String name) {
super(source);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}2>. 定义listener
@Component
public class MyEventListener implements ApplicationListener<MyEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(MyEvent myEvent) {
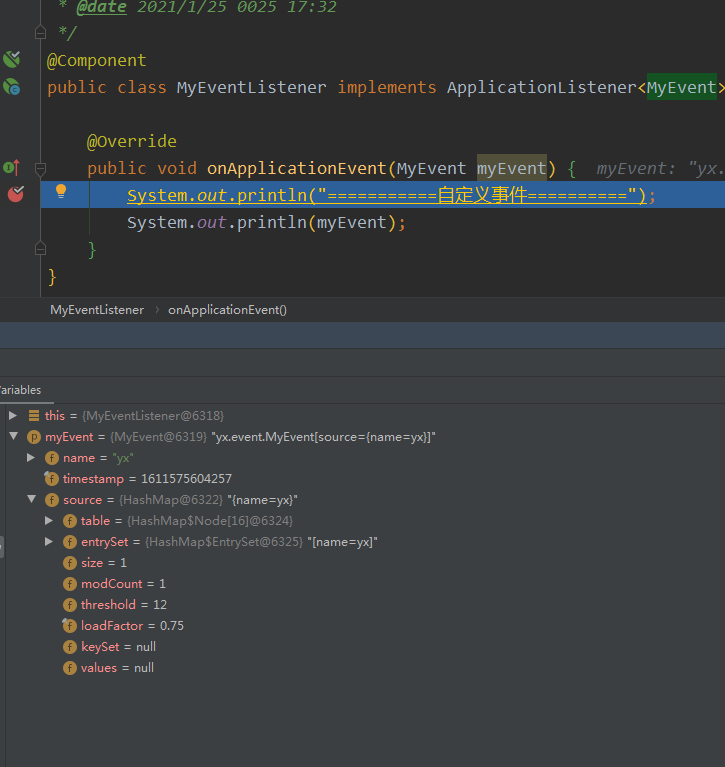
System.out.println("===========自定义事件==========");
System.out.println(myEvent);
}
}要点:ApplicationListener的事件泛型为 MyEvent,MyEventListener 要加上@Component
3>. 发布事件
@Autowired
private ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
@PostMapping("/get")
public BaseResponse get(){
Map res = new HashMap<>();
res.put("name","yx");
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new MyEvent(res,"yx"));
return BaseResponse.success(res);
}4>. 效果
3). 基于注解实现
1>. 事件定义一样的
2>. listener定义不一样,不用实现接口了
@Component
public class MyEvent2Listener {
@EventListener(classes={MyEvent2.class})
public void listen(MyEvent2 event){
System.out.println("MyEvent2Listener。。监听到的事件:" + event);
}
}3>. 发布事件,使用注解实现的话,idea左侧会有提示具体的监听地方,点击就进去了,如下图 MyEvent2的发布
4>. 效果一样
四. ApplicationContext在soul中的应用
1). 在用户使用注解 @SoulSpringMvcClient(path = "/test/**") 将用户端的路由信息同步到admin时,使用了ApplicationContext的ContextRefreshedEvent事件,作用是在bean初始化的时候,判断配置文件是否是全部代理,进行数据同步操作
@Slf4j
public class ContextRegisterListener implements ApplicationListener {
...
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(final ContextRefreshedEvent contextRefreshedEvent) {
if (!registered.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return;
}
if (soulSpringMvcConfig.isFull()) {
post(buildJsonParams(soulSpringMvcConfig.getContextPath()));
}
}
private void post(final String json) {
...
}
}2). 在admin模块大量使用自定义事件DataChangedEvent,在DataChangedEvent里面加入事件类型,配置组等概念
public class DataChangedEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private DataEventTypeEnum eventType;
private ConfigGroupEnum groupKey;
}并在 DataChangedEventDispatcher 中实现 ApplicationListener接口,监听事件,并根据事件类型的不同进行具体的数据发送
@Component
public class DataChangedEventDispatcher implements ApplicationListener, InitializingBean {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private List listeners;
public DataChangedEventDispatcher(final ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
public void onApplicationEvent(final DataChangedEvent event) {
for (DataChangedListener listener : listeners) {
switch (event.getGroupKey()) {
case APP_AUTH:
listener.onAppAuthChanged((List) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case PLUGIN:
listener.onPluginChanged((List) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case RULE:
listener.onRuleChanged((List) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case SELECTOR:
listener.onSelectorChanged((List) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
case META_DATA:
listener.onMetaDataChanged((List) event.getSource(), event.getEventType());
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected value: " + event.getGroupKey());
}
}
}
...
}实现 InitializingBean 接口是为了在初始化的时候,根据配置文件,实例化相应的数据同步方式,也就是 定义成员变量 listeners
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
Collection listenerBeans = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(DataChangedListener.class).values();
this.listeners = Collections.unmodifiableList(new ArrayList<>(listenerBeans));
}具体的使用还有很多种,根据需求可以灵活做出调整,最常见的使用还是,定义事件,监听事件,统一处理
版权声明:本文由星尘阁原创出品,转载请注明出处!